Introduction:
In the ever-evolving landscape of the business world, organizations are constantly seeking innovative ways to maximize their potential and achieve sustainable growth. One of the most critical aspects of this pursuit lies in the effective management of human resources. As businesses recognize the pivotal role their employees play, they are increasingly turning to competence-based management practices to unlock their workforce’s full potential.
This article delves into the world of competence-based management, exploring its significance and impact in modern organizations. We will begin by examining the importance of competence-based role descriptions, outlining how they enhance workforce productivity and streamline talent acquisition efforts. Then, we will explore the growing use of competence-based assessments in the modern organization, highlighting their role in nurturing talent, optimizing performance, and promoting continuous improvement. Finally, we will explore the synergistic approach of combining competence-based practices with situational leadership techniques to cultivate world-class performance within an organization.
1: Competence-Based Role Descriptions
1.1 The Shift from Traditional Job Descriptions
Traditionally, job descriptions focused solely on outlining tasks and responsibilities associated with a particular role. However, as businesses adapt to the rapidly changing market demands and competition, they are realizing that merely defining tasks falls short in fostering a dynamic and agile workforce. The transition from job descriptions to competence-based role descriptions marks a paradigm shift in human resource management.
1.2 Understanding Competence-Based Role Descriptions
Competence-based role descriptions are comprehensive frameworks that go beyond task-oriented definitions. These descriptions encompass a spectrum of skills, knowledge, behaviors, and attributes required to perform a job efficiently. By emphasizing competencies, organizations can map out a more holistic and strategic approach to talent management.
1.3 Key Components of Competence-Based Role Descriptions
Core Competencies: Core competencies are fundamental skills and attributes that align with the organization’s values and long-term objectives. These skills serve as the foundation for effective performance in any role within the organization.
Role-Specific Competencies: Each position within an organization demands specific competencies that cater to the unique demands of the role. Role-specific competencies provide a clearer roadmap for employees to excel in their positions.
Behavioural Competencies: Soft skills, such as communication, leadership, adaptability, and teamwork, play a crucial role in defining an individual’s success in any given role. Behavioural competencies enrich the organization’s culture and promote a positive work environment.
1.4 Advantages of Competence-Based Role Descriptions
Improved Talent Acquisition: Competence-based role descriptions enable organizations to articulate their requirements more precisely, attracting candidates who align with the company’s values and long-term goals. This reduces the risk of hiring mismatches and improves retention rates.
Employee Development and Training: Competence-based role descriptions provide a clear benchmark for evaluating employees’ current skills and identifying areas for improvement. This allows organizations to design targeted training programs, enhancing the workforce’s capabilities.
Performance Management: With competence-based role descriptions in place, organizations can assess employee performance more accurately. Objective evaluation criteria empower managers to provide constructive feedback and support employees’ growth.
1.5 Implementing Competence-Based Role Descriptions
Collaboration with Employees: In the process of creating competence-based role descriptions, involving employees and seeking their feedback fosters a sense of ownership and engagement.
Aligning with Organizational Goals: Competence-based role descriptions should align with the organization’s strategic objectives, ensuring that each role contributes to the overall success of the company.
Flexibility and Adaptability: Competence-based role descriptions must be flexible enough to adapt to evolving business needs and accommodate changes in the industry.
Competence-based role descriptions have revolutionized the way organizations manage their human resources, placing a greater emphasis on skills, behaviours, and attributes rather than just task-oriented responsibilities. This paradigm shift in human resource management has proven to enhance talent acquisition, employee development, and performance management. By focusing on a more holistic approach to defining roles, organizations can nurture a dynamic and motivated workforce capable of driving the organization towards world-class performance. As we move forward, it is essential for organizations to recognize the significance of competence-based management and harness its power to stay competitive in an ever-changing business landscape.
2: Competence-Based Assessments in the Modern Organization
In today’s rapidly evolving business landscape, organizations are continuously striving to optimize their human resources to achieve maximum efficiency and productivity. Traditional job descriptions and performance evaluations are no longer sufficient to gauge an employee’s capabilities and potential within an organization. As a result, a shift towards competence-based assessments has emerged, focusing on the skills, knowledge, and behaviours that directly impact job performance. This chapter delves into the significance and implementation of competence-based assessments in the modern organization.
2.1. Understanding Competence-Based Assessments:
Competence-based assessments represent a systematic approach to evaluating an individual’s performance, focusing on their abilities to perform specific tasks and duties effectively. Instead of merely relying on job titles and responsibilities, this method centers on the practical demonstration of skills and behaviors relevant to the role. This shift in focus enables organizations to better align individual capabilities with the overall business strategy, fostering a culture of continuous learning and development.
2.1.1 Key Components of Competence-Based Assessments:
Competence-based assessments involve the identification of core competencies required for success in a particular role. These competencies can be broadly classified into technical, behavioral, and interpersonal skills. While technical competencies cover job-specific knowledge and expertise, behavioural competencies address traits like adaptability, problem-solving, and communication. Interpersonal competencies, on the other hand, evaluate an individual’s ability to collaborate and work effectively in a team.
2.1.2. Designing Effective Competence Frameworks:
To implement competence-based assessments successfully, organizations must establish clear and comprehensive competence frameworks. These frameworks outline the expected behaviors and skills for each role within the organization. Collaborative efforts involving HR professionals, subject matter experts, and employees themselves are crucial in developing these frameworks to ensure they accurately represent the reality of the workplace.
2.2. The Advantages of Competence-Based Assessments:
Competence-based assessments offer several advantages over traditional evaluation methods, making them a powerful tool for modern organizations.
2.2.1. Enhancing Employee Development:
By focusing on specific skills and behaviours, competence-based assessments provide employees with valuable feedback on their strengths and areas for improvement. This feedback, in turn, aids in developing personalized training and development plans, fostering continuous growth within the organization.
2.2.2. Effective Performance Management:
Traditional performance evaluations often suffer from biases and subjectivity, leading to discrepancies in recognizing top performers. Competence-based assessments mitigate these issues by basing evaluations on measurable and observable skills, creating a fairer and more accurate performance management system.
2.2.3. Better Talent Acquisition and Succession Planning:
When competence frameworks are well-defined, they become valuable tools for talent acquisition and succession planning. HR professionals can use these frameworks to identify candidates with the right skills and potential for future leadership roles.
2.2.4. Supporting Organizational Agility:
In an ever-changing business environment, agility and adaptability are critical. Competence-based assessments help organizations identify employees who possess these essential qualities, allowing them to respond swiftly to market dynamics and evolving demands.
2.3. Implementing Competence-Based Assessments:
A successful transition to competence-based assessments requires careful planning and execution. Several steps can guide organizations in adopting this approach effectively.
Define Clear Objectives:
Before embarking on the implementation process, organizations must identify their objectives for adopting competence-based assessments. Whether it is to improve performance, foster innovation, or support succession planning, clarifying these objectives will drive the entire process.
Develop Competence Frameworks:
As mentioned earlier, creating robust competence frameworks is crucial. Involve subject matter experts and key stakeholders in the process to ensure that the identified competencies align with the organization’s vision and goals.
Align with Training and Development:
Competence-based assessments should go hand in hand with training and development initiatives. The feedback obtained through assessments can be used to design tailored training programs that address specific skill gaps and enhance employee capabilities.
Integrate Technology:
Leveraging technology solutions can streamline the assessment process and facilitate data analysis. Utilizing specialized assessment software can provide valuable insights into employee performance, further aiding in decision-making and performance management.
Competence-based assessments have become a vital tool for modern organizations to thrive in a dynamic and competitive business landscape. By shifting the focus from traditional job descriptions to observable skills and behaviours, organizations can optimize talent management, foster employee development, and achieve world-class performance. As businesses continue to evolve, embracing competence-based assessments will undoubtedly become a cornerstone of success in the modern workplace
3: The Use of Situational Leadership Practices in Growing and Realizing an Organization with World-Class Performance
In the fast-paced and competitive world of business, organizations are constantly seeking ways to improve their performance and achieve world-class status. One crucial aspect that plays a significant role in the success of any organization is its leadership practices. Situational leadership, a widely adopted leadership model, has emerged as an effective approach in growing and realizing an organization’s potential for achieving excellence. This chapter will delve into the concept of situational leadership, its relevance in the modern organizational landscape, and how it can be utilized to drive an organization towards world-class performance.
3.1. Understanding Situational Leadership
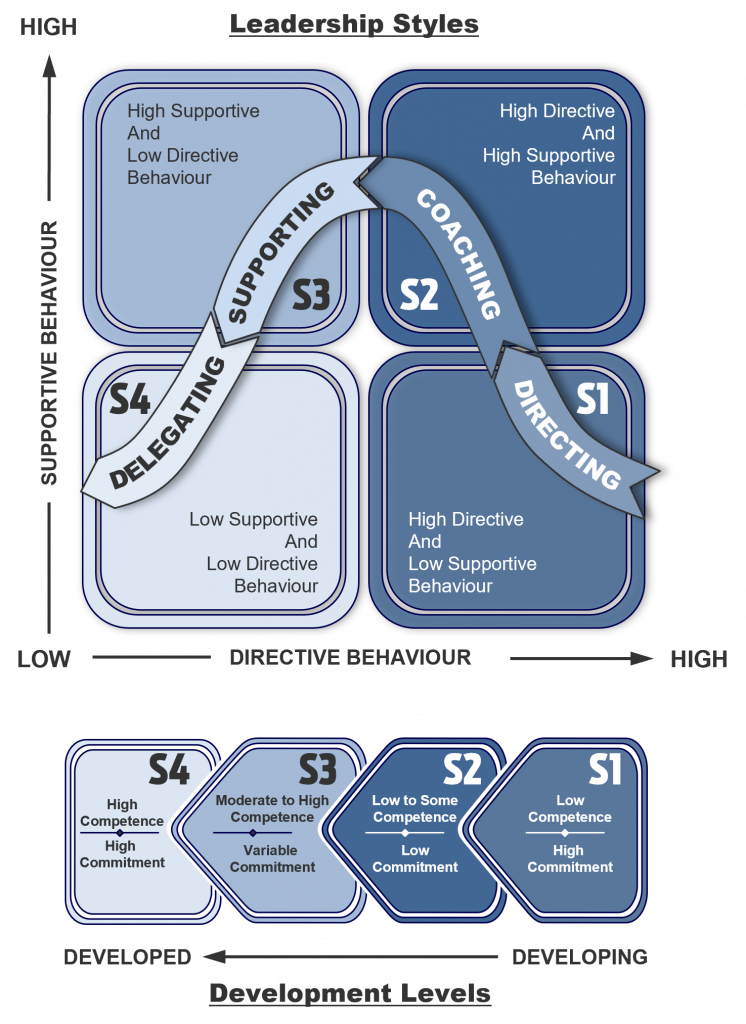
Developed by management experts Paul Hersey and Ken Blanchard in the late 1960s, situational leadership is a flexible leadership style that emphasizes adapting one’s approach based on the specific needs and maturity level of individual employees or teams. The fundamental premise of situational leadership is that there is no one-size-fits-all leadership style; rather, effective leaders tailor their behaviours to suit the unique circumstances and developmental stages of their followers.
The situational leadership model is characterized by four leadership styles, each of which corresponds to the varying degrees of support and direction provided by the leader:
Directing (Telling): In this style, leaders provide clear instructions and closely supervise their team members to ensure tasks are accomplished effectively. It is most suitable when dealing with inexperienced or low-maturity employees.
Coaching (Selling): As employees gain some level of competence, the coaching style involves providing guidance, explaining decisions, and fostering two-way communication to assist them in their development.
Supporting (Participating): When employees become more capable and confident, leaders can take a step back and provide support, encouragement, and recognition, empowering their team members to make decisions independently.
Delegating (Empowering): In this final stage, leaders entrust their experienced and highly competent employees with tasks and responsibilities, giving them autonomy and accountability in their roles.
The Role of Situational Leadership in Modern Organizations
In today’s dynamic and diverse workplace, situational leadership has gained prominence due to its adaptability and focus on individualized development. The traditional top-down, authoritative leadership approach is becoming less effective in many organizations, as employees increasingly seek a more collaborative and empowering work environment. Situational leadership aligns well with the needs and expectations of modern employees, as it places emphasis on mentorship, skill-building, and fostering a culture of continuous improvement.
Enhancing Employee Engagement: Situational leadership fosters a supportive and empowering environment, where employees feel valued, heard, and motivated to contribute to the organization’s success. This, in turn, leads to higher levels of engagement and commitment, resulting in increased productivity and reduced turnover rates.
Developing Future Leaders: By focusing on individual development, situational leadership helps identify potential leaders within the organization. As leaders adapt their styles to match their team members’ needs, they can groom emerging talents for leadership roles, ensuring a steady pipeline of competent leaders for the organization’s growth.
Nurturing a Learning Culture: A key aspect of situational leadership is the emphasis on continuous learning and skill development. Organizations that embrace situational leadership practices tend to foster a culture of learning, where employees are encouraged to seek new challenges and develop their capabilities, ultimately contributing to the organization’s competitive advantage.
3.2. Implementing Situational Leadership for World-Class Performance
To utilize situational leadership practices effectively in growing and realizing an organization with world-class performance, leaders must consider the following strategies:
Individualized Development Plans: Leaders should work closely with their team members to understand their strengths, weaknesses, and aspirations. Based on this knowledge, individualized development plans can be created to address specific needs and support employees’ career growth.
Communication and Feedback: Open and transparent communication is vital for successful situational leadership. Regular feedback sessions between leaders and team members help in understanding progress, addressing challenges, and aligning expectations.
Agile Leadership: Situational leaders must be agile and adaptable, capable of quickly assessing changing circumstances and adjusting their leadership styles accordingly. This agility allows leaders to respond effectively to the dynamic nature of the business environment.
Continuous Improvement: The situational leadership model itself is iterative, and leaders must continuously refine their approaches based on the evolving needs of their teams. Regular self-assessment and a commitment to improvement are essential for successful implementation.
Situational leadership offers a powerful and versatile framework for driving an organization towards world-class performance. By prioritizing individual development, fostering a learning culture, and adapting leadership styles to suit specific situations, organizations can create a motivated, engaged, and high-performing workforce. Embracing situational leadership practices is not only beneficial for employees’ growth and development but also critical for an organization’s sustained success in an ever-evolving business landscape. As more organizations recognize the value of situational leadership, we can expect to witness a paradigm shift in the way leadership is practiced, leading to a new era of world-class performance in the corporate world.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the triumvirate of competence-based role descriptions, competence-based assessments, and situational leadership practices serves as a powerful catalyst for achieving world-class organizational performance. Each can and often does stand alone, but when deployed as an integrated system there is a genuine force multiplying effect. Many organizations believe they already have this, very few in truth have real integrated systems with good processes at all steps and a high-yielding performance as a result. By meticulously aligning roles with competencies, objectively assessing performance, and adopting adaptable leadership styles, organizations can optimize their human resources and unlock their true potential. Embracing these practices fosters a culture of excellence, empowers employees, and propels organizations toward unparalleled success in the dynamic business landscape of today and tomorrow.

